What is a Standard Gain Horn Antenna?
A Standard Gain Horn Antenna is one of the most widely used reference antennas in RF and microwave engineering. Known for its simple geometry and predictable performance, it provides a stable, repeatable gain value across a defined frequency band. Engineers and researchers often rely on standard gain horns for calibration, measurement, and system validation.
Structurally, a standard gain horn is a flared waveguide that efficiently transitions electromagnetic energy into free space. Unlike many other antenna types, its gain characteristics are precisely defined and traceable, which makes it a trusted tool in laboratories, testing facilities, and field applications.
Key Features and Advantages:
-
Accurate Gain Reference – Each horn is designed to provide a well-documented gain value, essential for antenna calibration and comparison.
-
Broad Frequency Coverage – Standard gain horns are available in frequency ranges from a few GHz up to millimeter-wave bands.
-
Low VSWR and Stable Patterns – They offer excellent impedance matching and consistent radiation patterns.
-
Applications – Commonly used in antenna calibration, EMC testing, radar cross-section measurements, and wireless system validation.
At AO Microwave, we supply a wide range of Standard Gain Horn Antennas covering frequencies from 1GHz up to 110GHz. Our designs ensure precision, mechanical stability, and long-term reliability. We also provide customized horn solutions tailored to specific bandwidths, polarization, and connector/flange requirements—meeting the needs of aerospace, defense, telecommunication, and research institutions.
Whether you are conducting laboratory measurements or integrating antennas into demanding systems, a Standard Gain Horn Antenna remains the gold standard for accuracy and reliability.
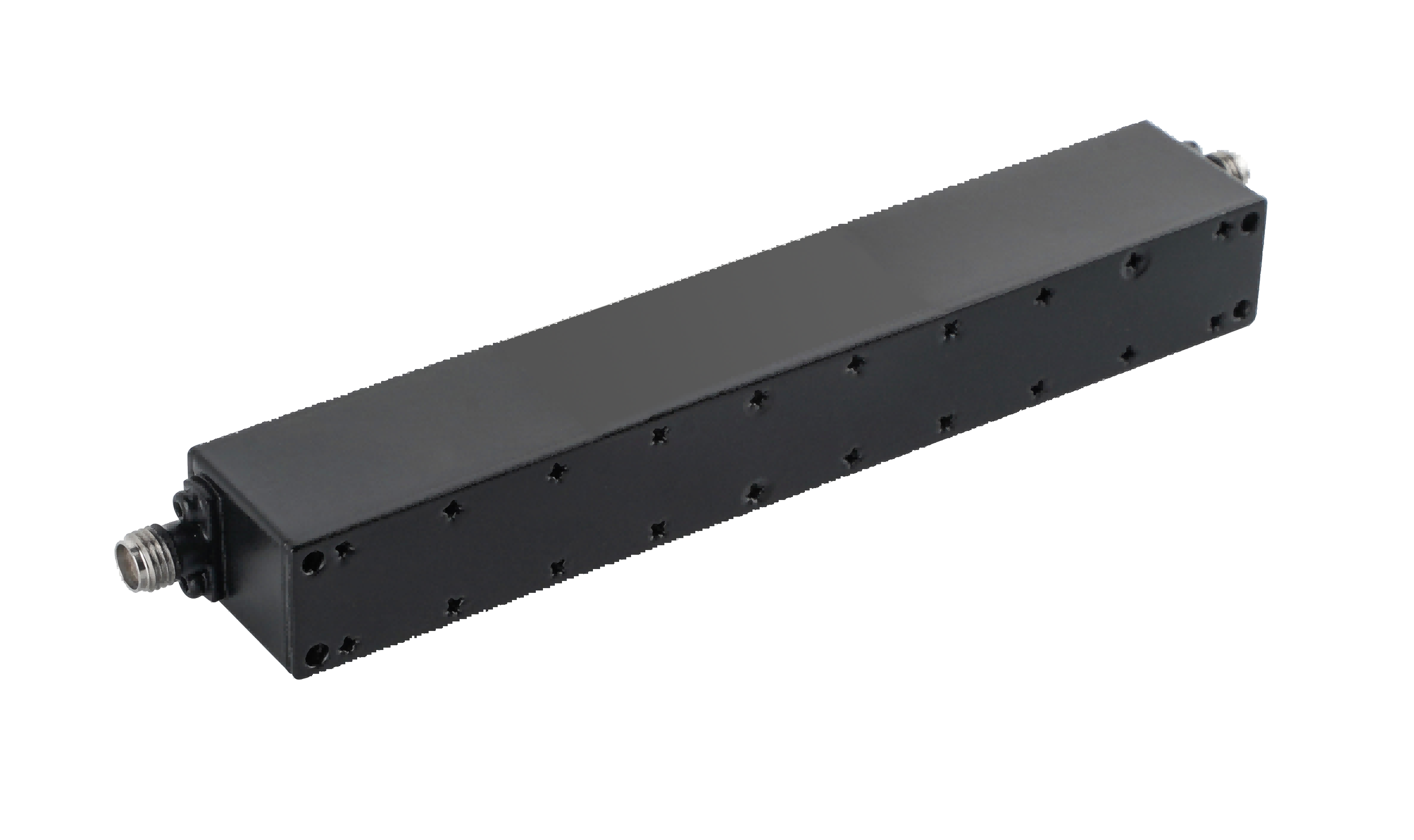 What Types of Coaxial Suspension Line Filters Are Available for RF and Microwave Systems?
What Types of Coaxial Suspension Line Filters Are Available for RF and Microwave Systems?
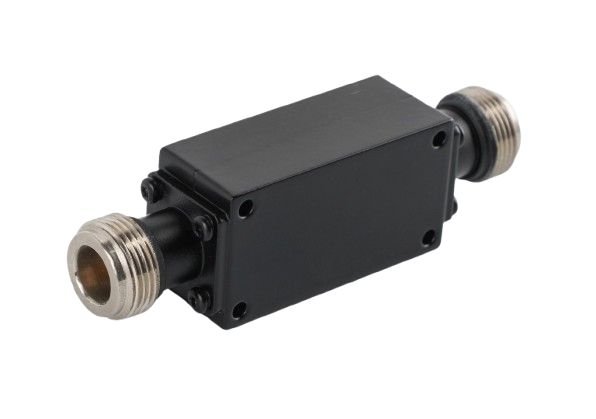 Why Are Coaxial Suspension Line Filters the Right Choice for High-Performance RF Systems?
Why Are Coaxial Suspension Line Filters the Right Choice for High-Performance RF Systems?
 What's the Coaxial Suspension Line Filter?
What's the Coaxial Suspension Line Filter?
 How to Choose a Log-Periodic Antenna for Long-Range Communication?
How to Choose a Log-Periodic Antenna for Long-Range Communication?

