Why Screws Used in Millimeter-Wave Products Are Different
When it comes to millimeter-wave (mmWave) components, every small detail matters — even the screws. Unlike standard fasteners, the screws used in high-frequency products such as WR22, WR19, WR15, WR12, and WR10 waveguide components are specifically engineered to maintain performance integrity and reliability under extreme conditions.
Precision Materials for Precision Frequencies
The screws commonly used in mmWave assemblies are made from SS304 stainless steel, a material known for its excellent corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, and dimensional stability. These characteristics are crucial in environments where temperature fluctuations, humidity, and mechanical stress could easily compromise the connection quality.
Preventing Signal Loss and Mechanical Loosening
At frequencies above 40 GHz, even the smallest misalignment or loosened joint can lead to signal leakage or impedance mismatch. SS304 screws are designed with anti-loosening properties, ensuring a stable and secure connection between mating waveguide flanges or precision housings. This helps maintain consistent performance over time and prevents unwanted degradation in signal transmission.
Designed for Long-Term Reliability
Millimeter-wave systems are often deployed in aerospace, radar, telecommunication, and research applications where maintenance access can be difficult. The corrosion-resistant nature of SS304 ensures that these fasteners can withstand harsh environments and prolong equipment life, reducing maintenance frequency and ensuring stable long-term operation.
In summary, the difference between ordinary screws and mmWave-specific SS304 screws lies in their precision, material performance, and engineering purpose. In high-frequency environments, these details are not just mechanical — they are fundamental to maintaining electrical integrity and overall system reliability.
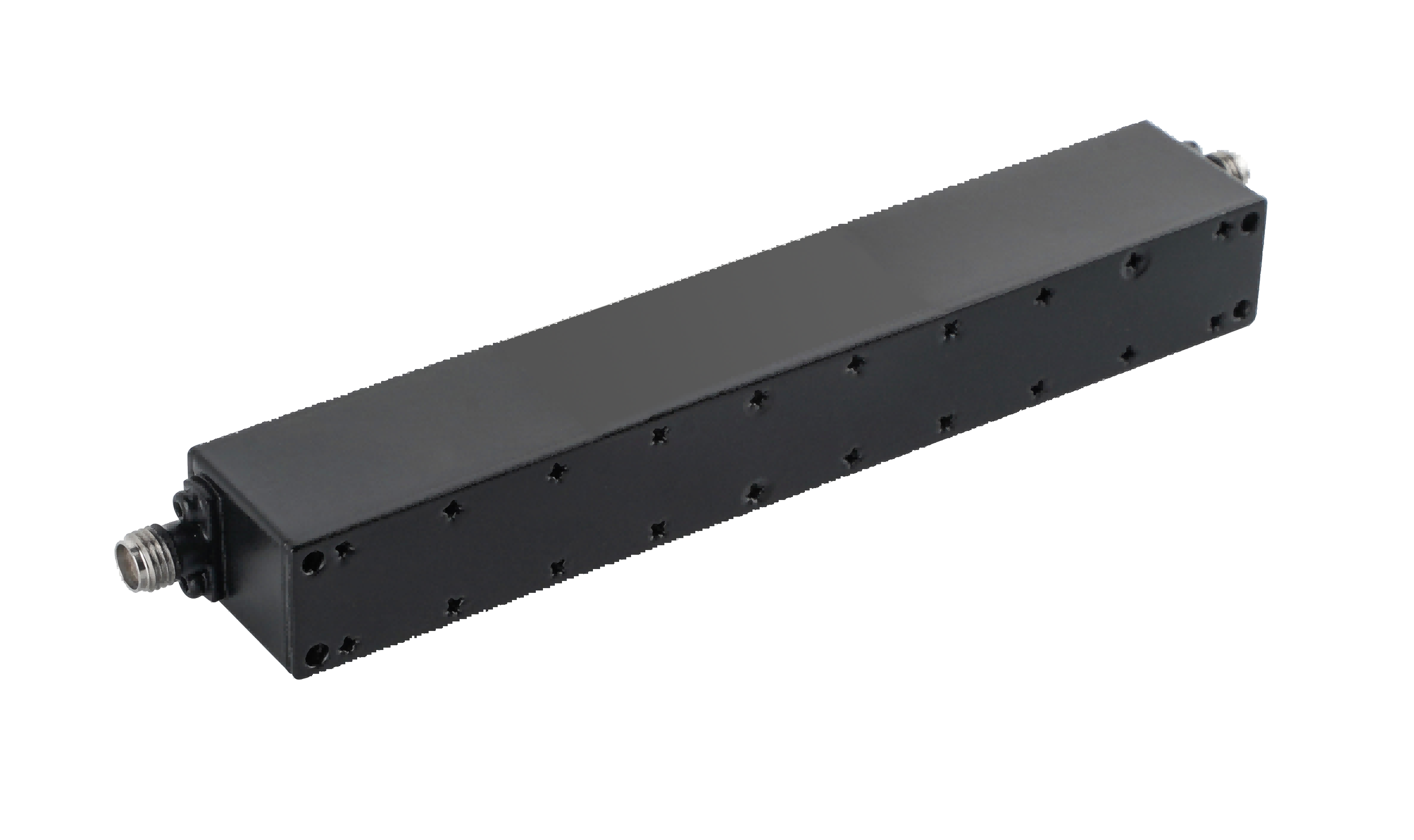 What Types of Coaxial Suspension Line Filters Are Available for RF and Microwave Systems?
What Types of Coaxial Suspension Line Filters Are Available for RF and Microwave Systems?
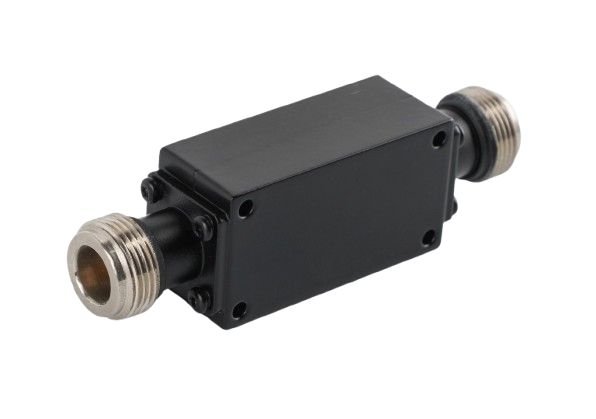 Why Are Coaxial Suspension Line Filters the Right Choice for High-Performance RF Systems?
Why Are Coaxial Suspension Line Filters the Right Choice for High-Performance RF Systems?
 What's the Coaxial Suspension Line Filter?
What's the Coaxial Suspension Line Filter?
 How to Choose a Log-Periodic Antenna for Long-Range Communication?
How to Choose a Log-Periodic Antenna for Long-Range Communication?

