Waveguide vs. Coaxial Components: What to Use and When
In RF and microwave systems, both waveguide and coaxial components play critical roles in signal transmission. Choosing the right solution depends on your system’s frequency, power level, installation environment, and mechanical constraints. Understanding the key differences can help engineers make more effective and cost-efficient design choices.
Waveguide components offer extremely low insertion loss and high power-handling capability, especially in high-frequency ranges—typically above 10GHz. They're ideal for radar systems, satellite communications, and aerospace applications where performance is paramount and precision is non-negotiable. However, waveguides are rigid, larger in size, and often require more careful alignment and mounting.
Coaxial components, on the other hand, are more compact, flexible, and easier to install, especially in lower-frequency systems or in test setups. They provide excellent broadband performance and are widely used in telecom, EMC testing, and lab environments. Yet, at millimeter-wave frequencies or under high-power demands, coaxial solutions may face greater losses and limitations.
At AO Microwave, we manufacture a full line of both waveguide and coaxial solutions—adapters, loads, attenuators, filters, and antennas—covering frequencies from DC up to 110GHz. More importantly, we provide custom engineering support to help you select and optimize the right component for your specific needs—whether it’s for a compact bench setup or a high-power airborne platform.
Need help determining which technology fits your application best? Contact our team (sales@aomicrowave.com) for expert advice and tailored solutions that bridge performance with practicality.
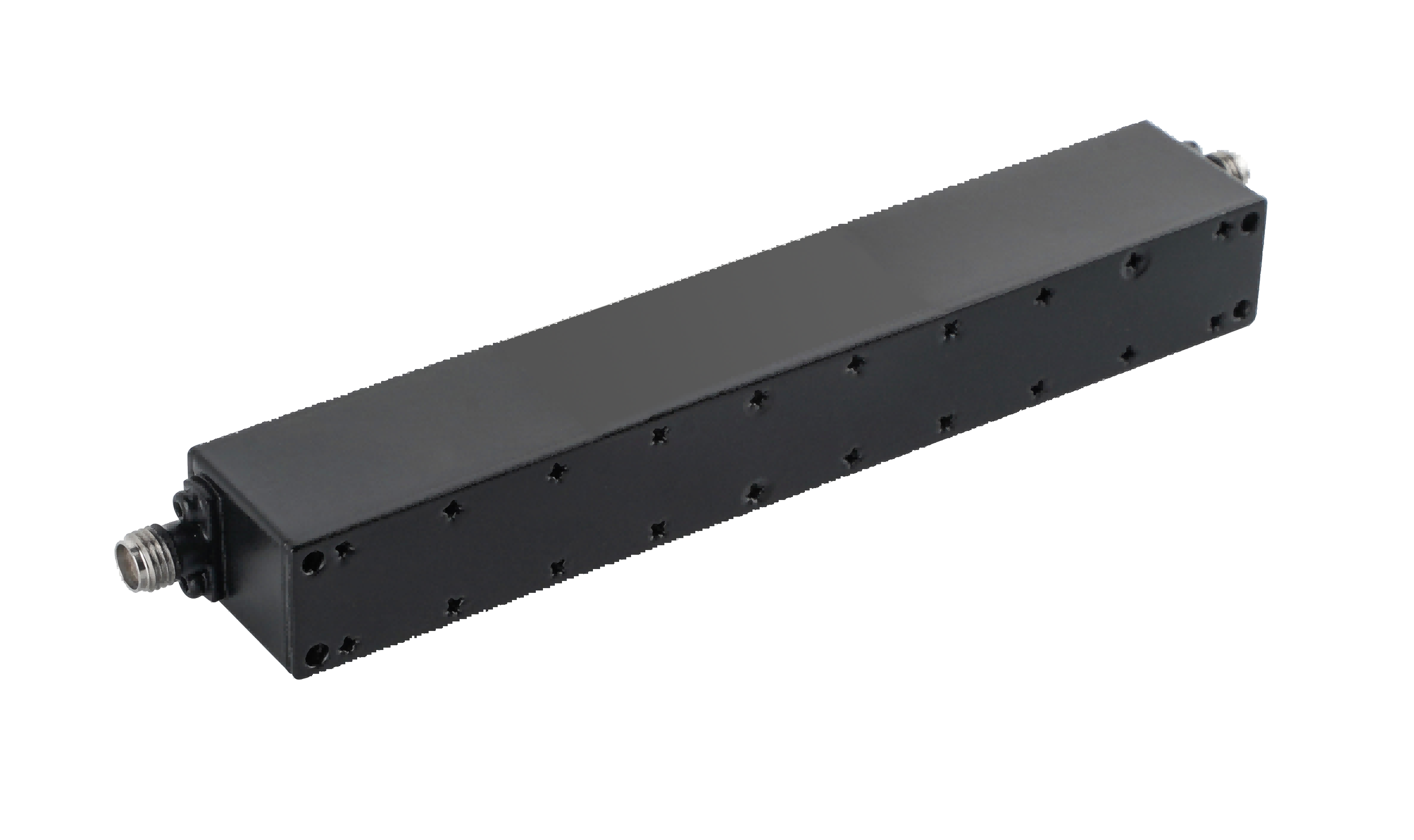
 What Types of Coaxial Suspension Line Filters Are Available for RF and Microwave Systems?
What Types of Coaxial Suspension Line Filters Are Available for RF and Microwave Systems?
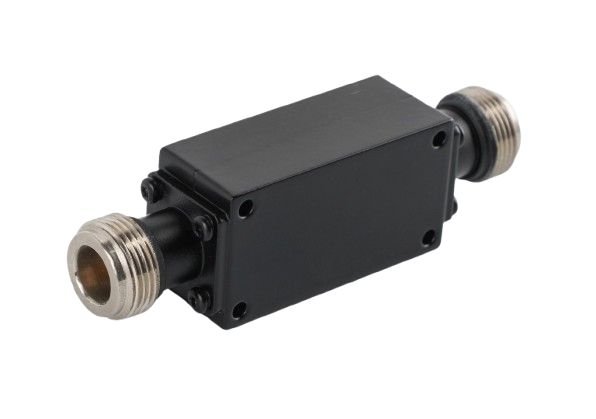 Why Are Coaxial Suspension Line Filters the Right Choice for High-Performance RF Systems?
Why Are Coaxial Suspension Line Filters the Right Choice for High-Performance RF Systems?
 What's the Coaxial Suspension Line Filter?
What's the Coaxial Suspension Line Filter?
 How to Choose a Log-Periodic Antenna for Long-Range Communication?
How to Choose a Log-Periodic Antenna for Long-Range Communication?

